NBFCs in India have emerged as one of the most dynamic forces shaping the nation’s financial ecosystem. Operating alongside traditional banks, they have bridged critical credit gaps and unlocked economic growth opportunities for millions—from micro-entrepreneurs and rural households to infrastructure developers. Over the past six years, the sector’s scale and influence have expanded remarkably, with NBFCs’ assets under management (AUM) nearly doubling from approximately ₹23 trillion in FY19 to ₹48 trillion as of FY25, reflecting a robust CAGR of 13.2%. This phenomenal growth underscores their transformation from a “shadow banking” system into a true powerhouse.
What is a non-banking financial company (NBFC)?
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 (originally Companies Act, 1956) of India, engaged in financial services such as loans and advances, investments, and asset financing without holding a banking license.
The working and operations of NBFCs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) within the framework of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. NBFCs play a pivotal role in delivering credit to segments often underserved by traditional banks.
Core activities include:
- Lending: Personal loans, SME finance, housing loans, microfinance, and asset loans.
- Investments: Acquisition of shares, stock, bonds, and participation in securities markets
- Asset Financing: Funding productive assets like vehicles and equipment that drive economic activity.
- Other Financial Services: Hire-purchase insurance business and chit-fund business
NBFCs vs. Banks: Key differentiators for the Indian consumer
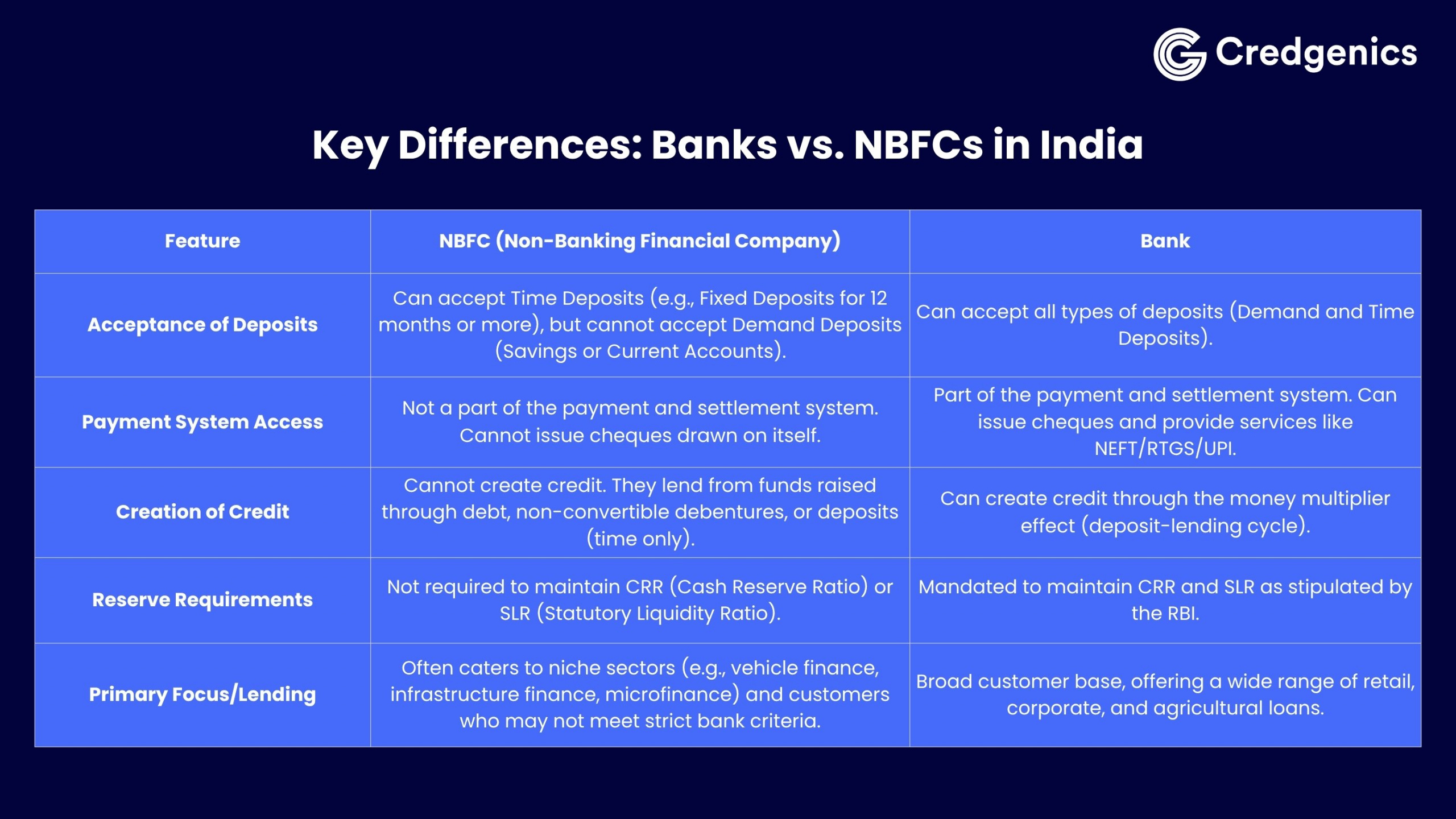
While both are regulated by the RBI, NBFCs enjoy greater flexibility in designing niche products and pricing strategies. They focus on specialized lending – catering to customer segments such as small businesses, rural borrowers, and first-time credit seekers. While banks provide a broader array of financial services. This specialization enables NBFCs to be faster, more customer-centric, and agile in risk-taking.
NBFCs don’t carry the deposit-related risks that banks do, allowing them to focus purely on lending and asset financing.
Recommended Read | How NBFCs are Transforming Consumer Lending in the Digital Age
Key catalysts driving NBFC growth in India
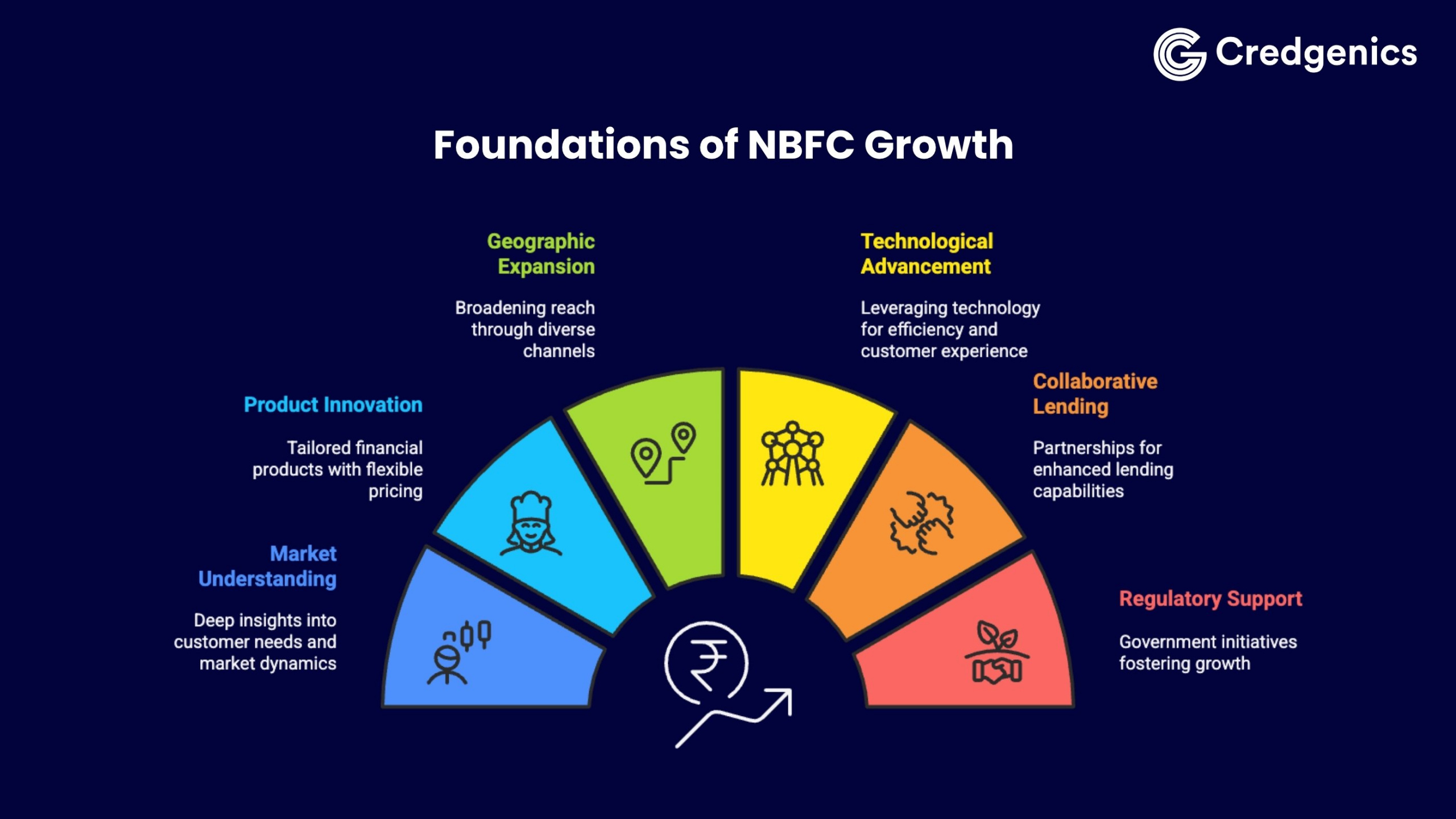
The growth of NBFCs in India has been propelled by a mix of deep market understanding, technology adoption, and supportive policy frameworks. NBFCs now contribute nearly 18–20% of total credit outflows in India, a figure that underscores their expanding systemic importance. Here are the fundamental drivers propelling their growth:
1. Deep market understanding and customer-centric approach
NBFCs have developed an intimate understanding of unorganized and underdeveloped market segments that traditional banks often overlook. By focusing on what customers truly need and ensuring last-mile delivery of financial products and services, they’ve created sustainable niches in underserved communities. This granular market intelligence enables them to design tailored solutions that are better equipped to address the real-world financial challenges.
2. Tailored product offerings with flexible pricing
Rather than offering one-size-fits-all solutions, NBFCs have mastered the art of customization and personalization. They analyze specific customer segments carefully and adapt their product offerings to meet unique characteristics and requirements. This targeted approach extends to pricing models as well, with NBFCs creating flexible structures that accommodate the financial realities of diverse borrower groups—from self-employed professionals to micro-entrepreneurs and farmers to small business owners.
3. Expanded geographic and channel reach
NBFCs are breaking geographical barriers by penetrating Tier 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4 markets where banking infrastructure remains sparse. They distribute loans across multiple customer touchpoints and have built truly omnichannel experiences that provide seamless sales and service 24/7. This phygital model, combining physical presence through local team members with digital platforms, ensures that financial services reach even the most remote corners of India.
4. Technology-driven efficiency and enhanced customer experience
The integration of technology has fundamentally transformed NBFC operations. Advanced fintech partnerships and digital tools have enabled these institutions to customize credit assessments with greater precision, reduce processing times dramatically, and offer instant loan approvals. This technological edge translates directly into superior customer experience and operational efficiency that rivals and often surpasses traditional banking.
5. Collaborative lending models
The introduction of co-lending norms by the RBI marked a watershed moment for the sector. These regulations enable banks and NBFCs to collaborate on priority sector lending (PSL), combining the funding strength of banks with the market reach and specialized expertise of NBFCs. This synergistic model has unlocked significant capital for underserved segments while maintaining prudent risk management.
6. Supportive government and regulatory initiatives
Government policy has been instrumental in creating an enabling environment for NBFC growth. Strategic initiatives addressing structural challenges in small business lending, including licensing account aggregators, launching the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), establishing UPI platforms, unveiling digital infrastructure like TReDS, and the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), and implementing GST, have collectively reduced friction in financial transactions and expanded the addressable market for NBFCs significantly.
How NBFCs are driving India’s economic growth
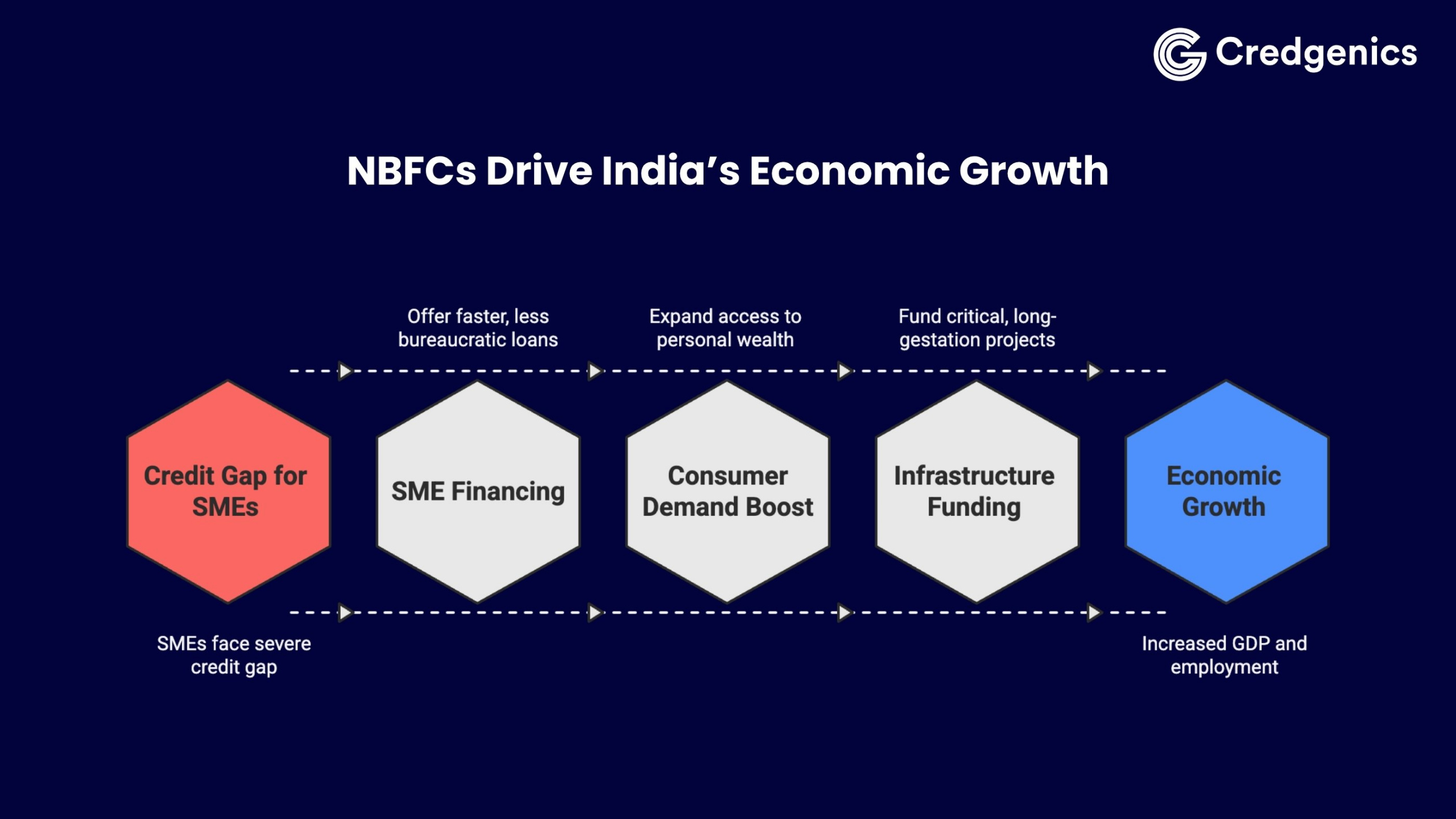
NBFCs in India are recognized as the ‘shadow banking’ system, but their impact on real economic activity is very real, driving credit penetration where it matters most.
1. Financing small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs and Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are the lifeblood of the Indian economy – contributing significantly to GDP growth and employment creation. However, they frequently face a severe credit gap to address their diverse needs. NBFCs play a vital role in bridging this gap by offering faster, less bureaucratic loan processing and accepting non-traditional collateral. These tailored financial products enable MSMEs to manage working capital, purchase inventory, and fund expansion, making NBFCs essential catalysts for business growth.
2. Boosting consumer demand and asset ownership
NBFCs have democratized access to personal wealth through instant personal loans and financing for consumer durables.
- Instant personal loans & consumer durable finance expand access to education, healthcare, and essential household assets.
- Asset Finance Companies (AFCs) drive sales of vehicles and equipment across agriculture, e-commerce logistics, and construction—linking credit to productive use and income generation.
3. Fueling infrastructure and developmental projects
Specialized NBFCs, particularly Infrastructure Finance Companies (IFCs), are crucial for India’s long-term developmental goals. By funding critical, long-gestation projects—including roads, renewable energy, urban infrastructure, logistics networks, telecommunications, and transportation—they ensure sustained capital formation. This support is vital because these projects often require highly specialized financing structures that traditional banks might hesitate to underwrite.
The role of NBFCs in empowering India’s financial inclusion journey

NBFCs in India play a crucial role in extending financial services to underserved and unbanked communities, helping bridge the gap toward true financial inclusion.
1. Reaching the underserved and rural markets
Unlike banks, NBFCs do not require a massive physical branch network to operate. They utilize phygital models, technology, and local agents to extend financial services beyond major urban centers. This reach is critical, as they cater to populations with limited or no formal credit history, providing them with the necessary credit to improve their livelihoods.
2. Specialized financial products for inclusion
- Microfinance Institutions (MFIs): Provide small, collateral-free loans that fuel micro-entrepreneurship, primarily reaching women in self-help groups (SHGs) and enabling economic independence at the grassroots level.
- Gold loan NBFCs: Offer highly accessible credit against household gold jewelry. This product is popular because it is secure, quick to process, and utilizes a commonly held asset, providing immediate liquidity without a high level of scrutiny.
3. Leveraging digitalization and fintech partnerships
Digitalization has exponentially amplified the reach of NBFCs. Using technology for faster loan application processing, digital KYC (Know Your Customer), and instant disbursal, NBFCs are creating a genuinely seamless customer experience. The rise of digital lending platforms, often powered by NBFCs, is key to achieving true financial inclusion at scale.
Related Read | Digital Lending: Empowering Rural, Semi-urban India Amid Financial Inclusion Challenges
The diverse landscape: Key types of NBFCs
The structure of the NBFC sector is highly diversified based on their core activity:
- Asset Finance Companies (AFCs): Focus on financing the acquisition of physical assets, like machinery, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
- Housing Finance Companies (HFCs): Regulated separately, these companies specialize exclusively in providing loans for housing and mortgage finance.
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs): Offer small loans and financial services to low-income borrowers.
- Core Investment Companies (CICs): Systemically important institutions primarily holding investments in group companies.
Technology as the transformative force in NBFC operations
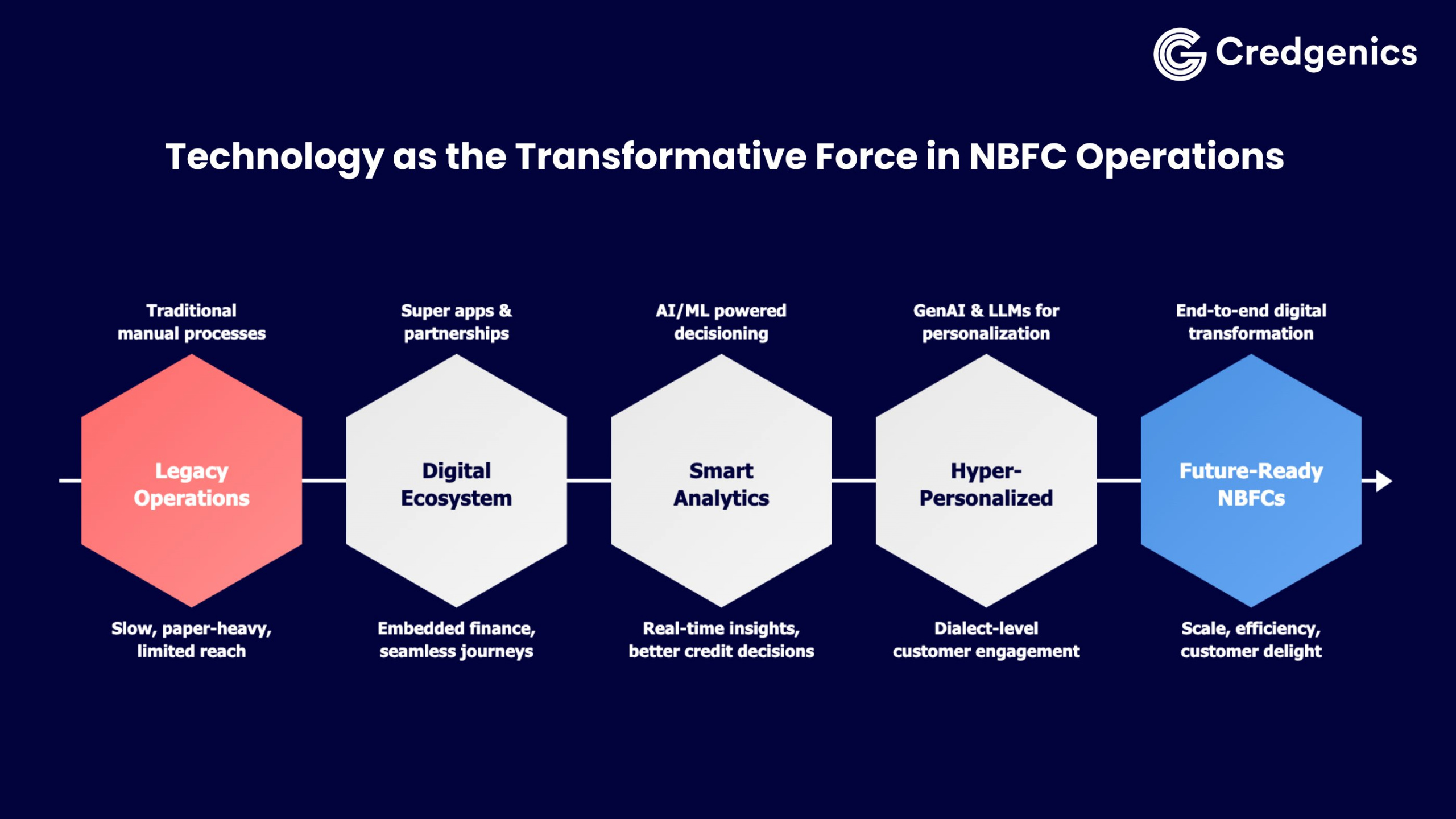
Technology has evolved from being a mere enabler to becoming the central nervous system of modern NBFC operations. It touches every aspect of the lending lifecycle—from customer acquisition and credit decisioning to disbursement, portfolio monitoring, and collections.
Key technologies reshaping the NBFC ecosystem:
1. Super apps and strategic partnerships
The emergence of super apps is redefining customer engagement in financial services. These one-stop digital platforms address customer needs from an end-to-end perspective, creating seamless journeys that were previously impossible. While super apps dominate banking and e-commerce, NBFCs are strategically embedding their products within these ecosystems, servicing customers through app-enabled journeys.
2. Frictionless credit enabling platforms and open protocols
The RBI’s frictionless credit enablement platform and the Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN) represent game-changing infrastructure for the financial services industry. These platforms dramatically ease integration efforts and provide rich, standardized data sources that can be leveraged across the entire loan lifecycle—from sourcing to servicing to collections. For NBFCs, this means faster onboarding, better credit decisions, and more efficient operations.
3. Digital-first and paperless customer journeys
NBFCs are pivoting decisively toward seamless and integrated digital-first and mobile-first experiences. This transformation ensures operational ease, enables better controls, and delivers superior customer convenience. Paperless documentation, digital KYC, instant approvals, and immediate disbursements have become standard expectations rather than competitive differentiators.
4. Analytics as a strategic competitive advantage
Data analytics has emerged as mission-critical across multiple business functions:
Sourcing: Pre-approved databases enable faster sanctions and more attractive customer offers
Customer Lifetime Value Optimization: Analytics maximize the long-term value of customer relationships, optimize product penetration, enable strategic partnerships, and facilitate successful cross-selling and up-selling initiatives
Credit Decisioning: The integration of financial and non-financial data sources has revolutionized credit assessment, dramatically improving the accuracy of scorecards and enabling NBFCs to serve previously “unscorable” segments
Portfolio Monitoring: Real-time, accurate portfolio monitoring coupled with evolved Early Warning Systems (EWS) leads to proactive interventions and more effective collection strategies
5. Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs)
GenAI and LLMs represent the frontier of NBFC technology adoption. These technologies are critical for achieving scale while cost-effectively delivering hyper-personalized experiences. The ability to interact with customers at dialect and sub-dialect levels—understanding regional linguistic nuances—is transforming awareness campaigns, customer sourcing, service delivery, and collections.
Regulatory challenges and future outlook
While growth is strong, the NBFC sector operates with inherent risks, demanding sophisticated credit and risk management solutions.
1. Navigating liquidity and funding risks
NBFCs often face higher funding costs and are heavily dependent on market borrowing (issuing bonds and commercial paper). This reliance exposes them to higher liquidity and asset-liability management (ALM) risks, especially during periods of economic uncertainty. The RBI’s enhanced focus on the regulatory framework is designed to ensure stability and mitigate systemic risk across the sector.
2. Maintaining asset quality (Non-performing assets – NPAs)
The core challenge for any financial institution is managing credit risk. Due to their focus on riskier or unbanked segments, NBFCs must implement robust strategies for credit risk assessment and delinquency management. Advanced, AI-driven digital collection strategies are no longer optional, they are essential for proactive delinquency management and maintaining low Non-Performing Assets (NPAs).
Modern collections intelligence platforms use real-time data, predictive analytics, and machine learning to segment customers and personalize the recovery journey. This shift moves collections from a reactive process to a proactive, customer-centric one, balancing efficiency with the maintenance of customer trust.
Credgenics is at the forefront of this collections transformation for leading NBFCs. By integrating AI powered solutions, collections intelligence, legal process automation, and modular solutions, collections platforms like Credgenics turn delinquency management into a competitive advantage. This approach significantly reduces losses, improves overall asset quality, and provides crucial feedback that reinforces better lending decisions.
3. The future: Embracing digital transformation and hybrid models
The future of NBFCs is inextricably linked to technology. They must adapt to increasing competition from traditional banks and disruptive Fintech firms by accelerating their digital transformation. The industry is moving toward a hybrid, regulated model that leverages technology for both underwriting new business and efficiently recovering overdue payments, ensuring a resilient and tech-forward financial ecosystem.
RBI’s regulatory framework: The backbone of NBFC stability & growth
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) serves as the cornerstone of India’s financial architecture, ensuring that Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) operate within a sound, transparent, and resilient framework. As the primary regulator and supervisor, the RBI’s role extends beyond compliance—it is about building trust, sustaining growth, and safeguarding the stability of India’s credit ecosystem.
The RBI classifies NBFCs based on their size, activity, and systemic importance. Its oversight encompasses liquidity management, asset quality monitoring, and risk governance, while enforcing robust disclosure standards and stress-testing mechanisms.
Beyond regulation, the RBI also acts as a facilitator of modernization. Initiatives such as the Digital Lending Guidelines, co-lending models, and data-driven supervision promote transparency, consumer protection, and financial innovation. This balanced approach empowers NBFCs to innovate responsibly while maintaining financial discipline.
Ultimately, the RBI’s regulatory stewardship ensures that NBFCs remain both agile and accountable—fueling economic expansion while upholding the integrity of India’s financial system.
Related Read | RBI digital lending directions 2025: What NBFCs & fintechs must know
Conclusion: NBFCs – Anchoring India’s financial future
NBFCs in India stand at the heart of the country’s financial growth, expanding access to credit while complementing the banking system. Their continued success will hinge on three capabilities:
- Credit discipline through data-led underwriting and proactive risk management.
- Liquidity resilience via prudent asset-liability strategies and diversified funding.
- Smart collections using AI-driven, compliant recovery processes that balance efficiency with customer trust.
From Credgenics’ perspective, integrating collections intelligence, legal automation, and analytics can turn delinquency management into a competitive advantage—reducing losses, improving asset quality, and reinforcing better lending decisions.
As digital transformation accelerates, the convergence of AI, analytics, and open financial networks will reshape India’s financial landscape. Supported by fintech collaboration and RBI’s enabling regulation, NBFCs will remain a resilient, inclusive, and innovation-driven pillar of the nation’s financial ecosystem.




