The financial services industry operates with an implicit degree of calculated risk that arises from multiple levels of uncertainties in their operational ecosystem. When it comes to debt collections processes, the regular inflow of new debt, dynamic business scenarios, and the evolving regulatory environment add to the complexity. Moreover, changes in the economic landscape and the transition toward customer-centricity have compelled lenders to rethink their strategies and gradually transition toward the use of AI in debt collections.
Traditional approaches of using emails, phone calls, and in-person interactions based on a generic strategy for all borrowers are time-consuming, inefficient, and lead to a poor customer experience. However, a dynamic shift in technology is transforming the collections ecosystem. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are being leveraged to streamline processes and address lenders’ significant concerns. Deploying AI in collections mechanisms results in better performance, easy scaling, and higher efficiency. The role of AI in debt collections has grown tremendously and it is acting as a major factor driving the transformation.
Banks and other non-banking lending companies are modifying their response strategies to incorporate technology and gain a competitive edge. BFSI sector, along with Industrials and Automotive, Healthcare, and Retail, is expected to contribute 60% of the potential AI-driven value add to India’s GDP by FY 2026. Within BFSI, the FinTech market is emerging as a leading use case for the deployment of AI.
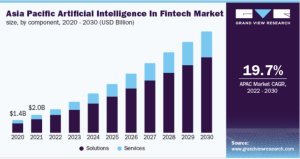
Source: Grand View Research
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging technology that can execute complex tasks that would otherwise require human intervention. Through analytics and machine learning capabilities, AI uses data to improve and optimize processes to improve collections performance. AI-powered applications can be trained to make decisions like humans and augment human input in data-driven tasks.
Debt collections teams are leveraging AI to overcome the challenges arising from archaic systems. They are able to make well-informed decisions based on past-performance data and customer profiling. Consequently, they deliver solutions that expedite debt settlement, while achieving efficiency and productivity.
The benefits of AI in debt collections
- Improved collections rates: Collections teams manage a large number of accounts with different sizes of debt influenced by unique circumstances. AI for predictive analytics can analyze historical data in tandem with prior borrower responses and enable collections teams to use this information to improve performance.
- Tailor-made outreach with automated communications: AI in debt collections can identify channel patterns and make faster decisions regarding borrower contact. Based on deeper understanding of the demographics and other factors affecting the borrower profile, lenders use AI to personalize the process for borrowers to meet their specific and unique needs.
- Optimized solutions: The pandemic has given rise to a whole new category of people in debt. Lenders need to scale to meet this influx of defaulters while maintaining a reasonable degree of service and empathy that a borrower needs. AI-powered tools help recovery teams to optimize the solution and strategy. They can process information faster through the statistical insights available and create effective roadmaps for different categories of borrowers. Scaling capabilities supercharged with AI enable them to prioritize customer communications and the delivery of adequate service support.
- Scaling up human-like interactions: One of the primary benefits of AI in debt collections is that many functions can be executed without the need for human intervention. For example, AI-powered chatbots can handle initial communication with debtors, gather the necessary information, and offer payment options. This can significantly reduce the workload on human resources, allowing them to focus on comparatively complex and creative tasks. Voicebots are another innovative technology solution, based on personalized engagement for debt collections. They use advanced capabilities such as NLP and dialogue management to revolutionize borrower outreach, enabling lenders to scale, optimize, and transform key elements of the debt collections journey.

Source: Credgenics
- Data analysis: AI-enabled automated debt collections processes can help algorithms analyze large volumes of data to identify patterns and predict debtor behavior. Proactive identification of at-risk accounts can augment the efforts to prevent them from becoming delinquent. This helps lenders develop strategies which are more effective in collecting debts. AI-powered chance predictors can detect the likelihood and propensity to pay, and the best time and method of communication can be devised. This helps lenders reduce the size of NPLs.
- Meeting compliance requirements: Risk mitigation is a major challenge for lenders as it impacts profitability and is closely connected to the legal framework within which lending institutions operate. AI algorithms can ensure that the debt collections process adheres to complex and rapidly evolving regulations. With automated controls in place, it becomes easier for debt collectors to mitigate fraud and the risk of compliance.
- Improved agent efficiency: Deployment of AI in contact centers can help in automating routine processes that free up human agents. It also provides insights on customers and refine strategies for future communications. As per a Gartner report, conversational AI will reduce contact center agent labour costs by $80 Billion in 2026, across the world.
Conclusion
In the long run, both lenders and borrowers will stand to gain from the modernization of debt collections as a result of deploying AI. The confluence of technology and behavioral science is a holistic means of understanding borrowers beyond the visible and utilize deeper knowledge to improve collection rates. Human biases and chances of error can be eliminated by logically automating debt collections and creating a customer-centric strategy. Lenders have already been generating value and improving customer experiences because of the impact of AI. As technology evolves, companies will have to recognize the growing need for prioritizing long-term relationships with borrowers and navigate their way through roadblocks in the processes by integrating AI in debt collections.
FAQs:
- How is AI used in debt collections?
Lenders are able to identify the best communication channels for borrower outreach and automate the strategy with minimal human intervention. Based on a study of borrower response patterns, lenders can create the right combination of multiple communication channels or deploy a single effective one. Consequently, collection rates improve, and business profitability increases. AI-powered data analysis techniques are used to predict borrower behavior and their propensity to pay. The deployment of AI in various stages of debt collections ultimately leads to improved recovery rates.
- How can automation improve debt collection?
One of the primary benefits of automation is that it streamlines the end-to-end collections process. Payment gateways and communications with customers can be integrated. A personalized outreach strategy can enhance the borrower experience and increase agents’ productivity. The deployment of chatbots and voicebots can simplify several repetitive tasks, giving human resources the opportunity to prioritize other functions that require creativity and human sensitivity. Lenders can instantly see an improvement in ROI as a result of implementing such a framework.
- How is AI modernizing the debt collections process?
AI-powered capabilities such as natural language processing and predictive analytics help lenders make informed decisions regarding their lending and collections mechanisms. Lenders are able to use technology to their advantage as a result of AI-based applications, ultimately leading to lowered NPLs and a fall in the number of repayment defaulters.