Contactless payment is a digital payment method that enables consumers to conduct transactions effortlessly by tapping or waving their contactless-enabled cards, smartphones, or wearable devices close to a compatible payment terminal. The proliferation of digital payments, coupled with the availability of numerous uncomplicated and convenient digital payment alternatives, has streamlined business operations for retailers, fostering financial inclusion and contributing to commercial and economic growth. While the term “contactless payment” might seem broad enough to encompass various payment methods, in the tangible world of plastic and silicon, it specifically pertains to well-defined parameters. These transactions commonly rely on technologies such as radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near-field communication, allowing communication with readers within a distance of approximately two to four inches. This proximity requirement adds a layer of security, ensuring that payments are intentional.
For the average consumer, the process of using contactless payment is remarkably straightforward. As long as the retailer has a contactless-enabled card reader, the mobile wallet or contactless-enabled card will automatically finalize the transaction when brought close to the reader.
The remarkable surge in contactless payments in India can be attributed to a convergence of influential factors:
a) Efficiency and convenience: The expeditious nature of contactless payments, which negates the necessity for physical card insertion or PIN entry, significantly expedites transaction times. Both retailers and consumers appreciate the streamlined and convenient nature of these transactions, rendering them an attractive choice for swift retail interactions.
b) Seamless technological integration: With the widespread adoption of smartphones and rapid advancements in mobile payment technologies, contactless payments have become accessible to a broader spectrum of retailers. Popular payment apps like Apple Pay and Google Pay feature contactless capabilities, offering customers a familiar and user-friendly platform. The simplicity of mobile phone usage, coupled with purpose-built applications for contactless payments, stands out as a key driver fostering retailer adoption.
c) Incentives and rewards: Financial institutions are actively incentivizing retailers to embrace contactless payment methods through loyalty programs, cashback incentives, and exclusive discounts. These enticing rewards serve as powerful motivators, encouraging businesses to increasingly embrace the simplicity and efficiency of contactless transactions.
d) Regulatory Support from RBI: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has played a pivotal role in propelling the adoption of contactless payments in India, especially among small retailers. By elevating the per-transaction limit for contactless card payments from INR 2,000 to INR 5,000, the RBI has incentivized businesses to adopt this secure and convenient payment mode. Introducing features like ‘Tap-and-Go’ and enhancing transaction limits for contactless mobile payments have further facilitated smoother transactions for both retailers and consumers. The adoption of this change by small retailers is noteworthy, as demonstrated by the increase in contactless transactions at MSMEs in January 2023 compared to January 2022—a rise of more than 125%.
Why is tap-and-pay safer than a card swipe? Watch this video by the Wall Street Journal to learn about the technology behind contactless payments!
The current state of contactless payments in India
India’s rapid adoption of contactless payments is garnering significant momentum, mirroring a global trend. The nation has quickly adopted contactless payment methods, driven by a confluence of strategic policy initiatives, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Key catalysts in this transformation include the introduction of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and initiatives like ‘Digital India. In the financial year 2023, almost 114 billion digital payments were recorded across India. This was a significant increase compared to the previous three years.
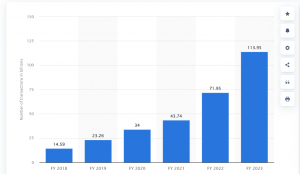
Total number of digital payments across India from financial year 2018 to 2023- (source: Statista 2023)
The impact of contactless payments on the retail sector is transformative, reshaping traditional transaction processes. This payment mode offers myriad advantages for small retailers, ranging from enhanced customer experiences and reduced operational costs to heightened security and expanded market reach. As consumers increasingly value the simplicity and security inherent in contactless payments, retailers must adapt to stay competitive in this evolving landscape. Embracing contactless payments not only accelerates transaction processes for retailers but also positions them as resilient and future-ready businesses.
Recent trends in the Indian contactless payments landscape
1) UPI is a big hit with retailers
In May 2023, India achieved a noteworthy milestone, surpassing 9.4 billion UPI transactions, as reported by the National Payments Corporation of India. The country stands out globally for having the highest volume of online transactions, predominantly driven by the widespread adoption of UPI-based payments. Notably, the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) and retail sectors experienced a remarkable 14% surge in UPI transactions. This was closely followed by a 9% growth in the fashion and lifestyle industry and a 12% increase in the food and beverage segment. This growth can be attributed to the seamless acceptance of digital payments by retailers and the growing comfort level of customers in engaging with digital transactions. The appeal lies in the simplicity and convenience offered by digital payment methods, with UPI emerging as a frontrunner in driving this transformative shift among retailers, effectively meeting their evolving needs.
2) Near-Field-Communications: The next big thing after UPI
In India, UPI payments have gained overwhelming preference over NFC, largely owing to considerations of accessibility and cost. The prevalence of NFC sensors in smartphones is limited, primarily found in higher-end models. However, the widespread use of QR codes and UPI apps has democratized access to contactless payments, allowing even more basic phones to participate in this payment method. The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has recently taken steps to bridge the gap between NFC and UPI payments. The introduction of UPI Tap & Pay, announced in September, extends the functionality of the Indian payment system, enabling users to make payments by simply tapping their devices on NFC-enabled QR codes at merchant locations. As this initiative becomes operational, it is anticipated that phone manufacturers will integrate NFC into more affordable handset models.
Some UPI payment apps now offer NFC payment capabilities. In 2022, Google Pay introduced a feature allowing users to make payments via NFC. The process involves a straightforward tap of the phone on the payment terminal, triggering the automatic launch of the Google Pay app, followed by payment confirmation. NFC not only facilitates swift and uncomplicated contactless payments but also presents a quick and efficient means of sharing content between devices. Although features like Android Beam have given way to newer technologies like Nearby Share, which operates on Bluetooth, the earlier NFC-based system showcased the technology’s potential for rapid peer-to-peer communication.
If you are looking to transform your debt collections strategy with the power of digital and data-powered insights, reach out to us to request an exploratory session at sales@credgenics.com or visit us at www.credgenics.com
FAQs:
1. What are contactless payments, and how do they work?
Contactless payments refer to a secure method of making transactions without physically swiping or inserting a card. This is typically done using contactless-enabled cards, smartphones, or wearables. The technology involved, such as NFC (Near Field Communication), allows for communication between the payment device and the terminal when nearby, facilitating a quick and convenient transaction.
2. Are contactless payments secure, and how do they protect against fraud?
Yes, contactless payments are secure. They use advanced encryption technology to protect sensitive information during transactions. Additionally, contactless transactions often have built-in security features like tokenization, where a unique token is generated for each transaction instead of transmitting actual card details. This makes it harder for fraudsters to gain access to valuable information.
3. What types of devices can be used for contactless payments?
Various devices support contactless payments, including contactless-enabled credit/debit cards, smartphones (via mobile payment apps like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay), and wearable devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers. As long as the device has the necessary technology, it can be used for contactless transactions.
4. How does contactless payment benefit consumers and businesses?
Contactless payments offer benefits to both consumers and businesses. For consumers, they provide a faster and more convenient way to make transactions, reducing the need for physical cash. Businesses benefit from faster transaction times, increased customer satisfaction, and improved operational efficiency. Contactless payments also contribute to a more hygienic and seamless payment experience, especially in a post-pandemic world.
5. What is the future of contactless payments, and what trends can we expect?
The future of contactless payments is expected to involve further integration with emerging technologies. Trends include increased use of biometric authentication, wider acceptance of cryptocurrencies, and the continued growth of mobile wallet usage. Additionally, innovations in wearables, advancements in security measures, and regulatory support are likely to shape the evolution of contactless payments.





