Bank branches may no longer be the first point of contact for an increasing number of people due to the way the financial services landscape is evolving. With more businesses converting to digital channels, customers have the choice of starting their financial journey on an accounting platform or an e-commerce platform. Through these avenues, they can effortlessly initiate deposit account setups, request debit cards, avail credit and cater to a significant portion of their financial needs. Interestingly, these platforms aren’t typically conventional banks. Rather, they are dynamic companies forging alliances with banks and technology providers to seamlessly integrate financial offerings into a unified, user-friendly, and hassle-free customer experience. This pioneering model of collaboration between banks, technology providers, and distributors of financial solutions via non-financial platforms is the driving force behind what’s been acclaimed as the evolution of embedded finance.
Understanding embedded finance: A paradigm shift in financial services
Embedded finance can be likened to the fusion of traditional financial services with non-financial platforms, seamlessly integrating banking, payments, insurance, lending, and more into everyday experiences. This transformative approach is realized through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that enable businesses to embed financial functionalities within their existing products or services. In simpler terms, it means that a user’s favorite ride-sharing app could potentially offer them a personalized loan option, or an e-commerce platform could extend instant credit at checkout, or a fitness app might assist a user in setting up an investment portfolio—all without leaving their respective digital ecosystems.
To understand embedded finance in a simple way, let us take an example: A customer uses a travel website to purchase their ideal vacation package. The entire transaction takes place within the travel app itself, saving the user from having to switch to a different banking app to finish the payment. The app leverages embedded finance to provide the user with multiple payment options, including installment plans, optimized foreign exchange rates, and even travel insurance—all powered by partnering financial institutions’ APIs. This streamlined experience eliminates the friction of toggling between various apps, offering convenience and personalized financial solutions in real-time. There are many such examples of embedded finance that can be understood to ascertain how it creates value for the customers and and financial institutions.
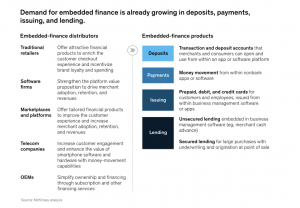
Source: McKinsey & Co.
Product offerings and distribution
Various business sectors are well-positioned to offer embedded finance, encompassing retailers, business software providers, online marketplaces, platforms, telecom enterprises, and original equipment manufacturers. These segments have witnessed a surge in both activity and innovation within the realm of embedded finance over the last couple of years.
Within this landscape, the demand spectrum is evolving, stretching from embedded-finance distributors to end consumers and encapsulating an array of deposit, payment, issuance, and lending products. Going beyond conventional financial offerings, novel applications are on the horizon. To illustrate this – embedded-finance distributors are venturing into providing prepaid cards to employees as an integral part of earned-wage access programs. They are enabling merchants to utilize their deposit accounts for swift payment settlements. Additionally, an innovative move entails providing on-the-spot funded debit cards to gig economy workers in order to facilitate their purchases for users of delivery service platforms.
As the journey of customer onboarding and product service transitions towards digitization, the embedded finance market is likely to expand. Simultaneously, the evolution of real-time risk analytics and advanced services is set to add further dimensions to this expansion. A McKinsey analysis states that products offering embedded finance could account for as much as 50% of banking revenue pools.
Reshaping fintech: The impact of embedded finance
The potential impact of embedded finance in India and on the global fintech industry is nothing short of transformative. Here are a few significant ways embedded finance is poised to transform the industry:
- Enhanced customer experience: By seamlessly integrating financial services into existing platforms, embedded finance offers unparalleled convenience and personalized solutions, elevating the overall customer experience.
- Democratizing financial services: Embedded finance has the power to extend financial services to underserved populations by leveraging non-financial platforms they already use regularly, thereby promoting financial inclusion.
- Innovation acceleration: The collaboration between fintech and non-financial companies fosters fertile ground for innovation. This partnership drives the creation of novel financial products and services tailored to diverse consumer needs.
- Data-driven insights: Embedded finance enables the collection of data from multiple touchpoints, granting insights that can be harnessed for enhanced risk assessment, targeted marketing, and predictive analytics.
- Ecosystem synergy: Fintech companies collaborating with non-financial entities create symbiotic ecosystems that cater to a wide range of customer needs under one digital roof.
- Disrupting traditional banking: As embedded finance blurs the lines between sectors, traditional banking models might be compelled to evolve, adopting more agile, customer-centric approaches.
The road ahead for embedded finance
The journey ahead for embedded finance is undoubtedly promising, but it also brings forth challenges that need careful consideration. Privacy concerns, data security, regulatory compliance, and the need for robust partnerships between fintech and non-financial companies are some of the hurdles that the industry must address to unlock the full potential of embedded finance.
Embedded finance marks a pivotal juncture in the evolution of fintech, transforming financial services from standalone entities into integral components of everyday experiences. It’s evident that embedded finance will not just change the fintech landscape but will also redefine how we envision and engage with financial transactions, propelling us into a future where financial services are seamlessly woven into the fabric of our daily lives.
FAQs:
- How does embedded finance benefit businesses and customers?
For businesses, embedded finance streamlines customer interactions by providing convenient financial services without redirecting customers to external platforms. This enhances customer loyalty and engagement. Moreover, businesses can generate additional revenue streams through partnerships with financial institutions. Customers benefit from a unified experience where they can access various financial products tailored to their needs within the platforms they already use.
- Is embedded finance secure and regulated?
Yes, embedded finance operates within the regulatory framework of financial services. Financial products integrated into non-financial platforms adhere to the same regulatory standards as traditional offerings. Security measures, such as encryption and authentication, are implemented to ensure the safety of financial transactions. Regulatory compliance and data protection remain integral components, ensuring that customers’ financial information is treated with the same level of confidentiality and security as in traditional banking channels.
- Can any business integrate embedded finance, or is there a specific criteria?
While various businesses can leverage embedded finance, certain criteria enhance its feasibility. Businesses with a customer-centric approach, a significant user base, and a digital platform infrastructure are well-suited. Additionally, businesses must forge partnerships with financial institutions to provide the necessary financial products and services. The integration process involves collaboration, technological integration, and adherence to regulatory standards to ensure a seamless and secure embedded finance experience.





