Banking as a Service (BaaS) facilitates the seamless integration of digital banking services into non-banking enterprises, empowering fintech and other entities to offer a range of banking services such as debit cards, loans, and payment services. This transformative concept reshapes the traditional banking value chain, unlocking avenues for new sources of growth. The adoption of Banking as a Service enables businesses to swiftly introduce specialized offerings to the market, addressing the dissatisfaction among customers with conventional banking services. This innovative approach has not only enhanced the speed of service delivery but also ushered in a new era of collaboration between traditional banks and non-banking entities, fostering a dynamic and customer-centric financial ecosystem.
The importance of BaaS
Banking as a Service is gaining significant traction as customers increasingly consider switching banks and exploring alternative financial services for different needs. Traditional banks, which previously owned the entire banking value chain, are now facing challenges due to the evolution of consumer demands and preferences. In light of rapid digital and e-commerce adoption, customers are seeking alternative financial solutions that better align with their needs and expectations. BaaS offerings are rapidly gaining ground by addressing these expectations and providing specialized propositions tailored to specific customer segments.
Exploring the BaaS model
Integration of financial services into non-financial platforms
BaaS enables the integration of financial services and products into non-financial digital platforms. This integration allows customers to access financial products seamlessly while engaging with their preferred non-financial activities. For example, customers can take out a small loan when booking a holiday on a travel site, or instantly purchase micro-insurance for newly acquired jewellery. Non-financial businesses can distribute these financial products under their brand, providing customers with a cohesive purchasing experience.
Distribution of financial products under non-financial brands
Financial institutions can embrace BaaS by establishing platforms that facilitate the distribution of financial products through non-financial partners. By utilizing low-cost, cloud-native, and scalable technology, financial institutions can reduce the cost of serving customers. This presents an opportunity for banks to reach a larger customer base while minimizing operational expenses.
Cost reduction and improved customer reach
Traditional financial institutions often struggle with high costs and inefficiencies in their technological assets. BaaS provides a solution by enabling banks to leverage innovative technology and reduce the cost of serving customers. This cost reduction allows banks to reach a greater number of customers at a significantly lower cost.
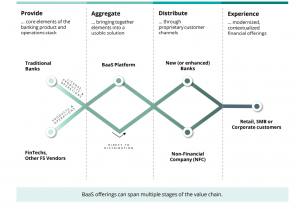
Source: Deloitte (‘Banking as a Service, Explained’)
Benefits of Banking as a Service
1. Innovation acceleration:
Banking as a Service (BaaS) allows for faster innovation in the financial sector. By seamlessly integrating digital banking services into non-banking businesses and fintech, BaaS enables the quick development and deployment of new financial products and services. This agility fosters a culture of innovation, allowing businesses to stay ahead of market trends and meet evolving customer expectations.
2. Market expansion and accessibility:
BaaS opens up opportunities for non-banking entities to provide a range of financial services without the need for a full banking infrastructure. This leads to increased market accessibility, allowing businesses to cater to a broader customer base. Fintech startups, for example, can leverage BaaS to offer banking services without the traditional barriers to entry.
3. Customer-centric solutions:
With BaaS, businesses can focus on delivering solutions that are tailored to the specific and evolving needs of customers. The flexibility offered by BaaS platforms allows for the faster creation of personalized financial products, enhancing the overall customer experience. This adaptability enables businesses to respond swiftly to changing customer preferences and market demands.
4. Cost efficiency and resource optimization
Utilizing BaaS reduces the need for non-banking entities to invest heavily in building and maintaining a comprehensive banking infrastructure. This leads to significant cost savings and efficient resource allocation. BaaS providers handle the intricacies of banking operations, allowing businesses to concentrate on their core competencies and strategic initiatives.
5. Collaboration and ecosystem development:
BaaS encourages collaboration between traditional banks, fintech, and various non-banking entities. This collaborative approach fosters the development of a vibrant financial ecosystem where different players contribute specialized services. Through partnerships and interoperability, businesses can create a comprehensive suite of financial solutions, offering customers a seamless and integrated experience.
How BaaS enables open banking
BaaS plays a crucial role in enabling open banking, which aims to enhance financial transparency and provide customers with more options. By opening their APIs to third-party developers, banks can facilitate the development of new services and foster innovation in the financial services industry.
Democratizing data and enhancing transparency
Digital transformation has democratized data and enabled greater transparency across industries, including financial services. BaaS platforms act as key components of open banking, allowing firms to provide customers with more financial transparency options. By opening their APIs, banks enable third parties to develop innovative services that enhance the customer experience.
Fostering better customer experiences
BaaS platforms enable the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial digital platforms. Customers increasingly rely on these platforms for various activities, such as e-commerce, travel, retail, healthcare, and telecommunications. By offering financial products within these platforms, customers can access a wide range of services under a single brand, simplifying their experience and enhancing convenience.
The outlook for the BaaS industry
Countries worldwide have started implementing open banking regulations, indicating a shift towards a more transparent financial services industry. Shared data and infrastructure are becoming the new expectations for consumers. Financial institutions that embrace BaaS platforms can stay ahead of the curve and unlock new revenue streams by monetizing their platforms.
In India, Banking as a Service (BaaS) is transforming the financial landscape by allowing non-banking entities to seamlessly integrate digital banking services into their offerings. This innovative approach enables fintech companies, businesses, and other non-banking entities to provide a range of financial services, including loans, payments, and debit cards, without the need for a full banking infrastructure. BaaS fosters collaboration between traditional banks and non-banking entities, unlocking new opportunities for market expansion, innovation, and customer-centric solutions. This digital evolution in banking is not only enhancing accessibility to financial services but also redefining the traditional banking value chain in India.
As per a report, total revenue for Banking as a Service (BaaS) will increase from US$1.7 billion in 2021 to surpass US$17.3 billion by 2026, excluding nontraditional banking services such as point-of-sale lending and customer-consented payment initiation services.
Conclusion: Embracing the BaaS opportunity
BaaS represents a great opportunity for financial institutions to adapt and thrive in the digital age by tapping into the power of a wider ecosystem. By partnering with non-financial businesses and integrating their services into non-financial platforms, banks can reach a larger customer base, reduce costs, and unlock new revenue streams. BaaS enables financial institutions to provide customers with innovative and personalized financial solutions while delivering a seamless customer experience. As the financial services industry continues to evolve, embracing the BaaS model is essential for staying competitive and driving growth in an increasingly digital world.
If you are looking to transform your debt collections strategy with the power of digital and data-powered insights, reach out to us to request an exploratory session at sales@credgenics.com or visit us at www.credgenics.com.
FAQs:
1. What is Banking as a Service?
Banking as a Service (BaaS) is a financial services model that allows non-banking entities to offer banking products and services without the need for a traditional banking infrastructure. In this model, fintech companies, retailers, or other businesses can leverage the capabilities of a banking platform to provide services such as payments, loans, and account management. BaaS enables these third-party providers to access and use the underlying banking infrastructure, including regulatory compliance and technology, to offer a seamless and integrated financial experience to their customers. This innovative approach fosters collaboration between traditional financial institutions and emerging fintech players, promoting the development of new, customer-centric financial solutions.
BaaS is characterized by its flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies while relying on banking partners for the underlying financial services. This model promotes innovation and competition in the financial industry, as it enables a diverse range of companies to enter the market and tailor financial services to meet the evolving needs of consumers. As a result, BaaS has the potential to drive greater efficiency, lower costs, and increase accessibility to financial services for a broader segment of the population.
2. How does Banking as a Service differ from traditional banking?
Banking as a Service (BaaS) differs from traditional banking in that it decouples banking functions from the traditional banking infrastructure. In a traditional banking setup, a financial institution provides end-to-end services, including account management, loans, and payments, often through physical branches. BaaS, on the other hand, allows non-banking entities to plug into a banking platform, accessing specific banking services without the need for a complete banking infrastructure. This modular and API-driven approach fosters innovation, allowing third-party providers to create tailored financial solutions without the constraints of building and maintaining a full-fledged banking system.
3. What are the benefits of adopting Banking as a Service for businesses?
Adopting Banking as a Service offers several benefits for businesses. Firstly, it accelerates time-to-market for financial products and services, as companies can leverage existing banking infrastructure rather than building it from scratch. Secondly, BaaS promotes agility and scalability, enabling businesses to scale their financial offerings quickly and efficiently. Additionally, BaaS facilitates cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for significant upfront investments in technology and regulatory compliance. Finally, BaaS fosters innovation by encouraging collaboration between traditional financial institutions and fintech disruptors, resulting in a more dynamic and competitive financial services landscape.





