Unlocking the potential of MSME lending in India
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are the backbone of India’s economy, contributing significantly to its growth and employment generation. However, MSMEs often face financial constraints that hinder their expansion and development. In recent years, the Indian government and financial institutions have recognized the importance of supporting MSMEs through improved access to credit. In response to the numerous hurdles they face, the government has initiated powerful measures aimed at empowering these enterprises, unlocking their true potential, and ensuring they have easier access to the financial support they need to flourish. MSME lending in India is at a stage where greater effort is required to enable the expansion of entities in the sector.
The present scenario of MSMEs in India
MSMEs contribute close to 30% to India’s GDP and make up 45% of the country’s exports. In addition, MSMEs employ millions of people, helping reduce the regional imbalance of employment in the country. Furthermore, this sector plays a pivotal role in bolstering other industries by supplying essential raw materials and supplementary goods. Historically, the MSME sector has served as a robust pillar for the Indian economy, endowing it with the fortitude to withstand global economic upheavals and confront challenges head-on.
A large percentage of MSMEs fall into the micro category, with a significant majority categorized as nano units. These encompass a diverse range of businesses such as corner stores, small clothing shops, eateries, mobile phone retailers, hair salons, beauty parlors, bakeries, confectioneries, hardware stores, auto accessory shops, pharmacies, and more. What is noteworthy is that many of these MSMEs operate as proprietorships, often lacking comprehensive income documentation. This underscores the urgent need for a renewed effort towards financial inclusion and a substantial increase in microcredit access for segments of society that are currently underserved.
While the central government has undertaken various credit and financial assistance programs to support small businesses within the MSME sector, the role of the private sector in bridging the gap between loan demand and supply, especially for micro and nano enterprises in rural and semi-urban areas, remains notably limited. Some of the areas in which the government has been implementing various schemes include:
- Credit support
- New enterprise development
- Formalisation
- Technological assistance
- Infrastructure development
- Skill development and training; and,
- Market assistance
The average loan size of MSMEs in India by segment is captured in the below image.
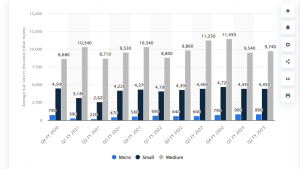
Source: Statista 2023
Challenges faced by MSMEs
Despite their significance, MSMEs face several challenges that can hinder their development and sustainability. Some of these are:
- Limited Access to Finance:
- Lack of Collateral: Many MSMEs lack the assets or collateral required to secure traditional bank loans. This limits their ability to raise capital for expansion or working capital.
- High Interest Rates: Even when they can access credit, MSMEs often face higher interest rates, which can erode profitability and make repayment challenging.
- Complex Borrowing Procedures: Traditional lending institutions may have complicated and lengthy application processes, making it difficult for small business owners to navigate.
- Inadequate Infrastructure:
- Limited Technology Adoption: MSMEs, particularly in rural areas, may struggle to adopt modern technologies, hindering their productivity and competitiveness.
- Logistical Challenges: Poor transportation infrastructure and inefficient supply chains can increase operational costs and hamper the delivery of goods and services.
- Market Access and Competition:
- Limited Market Reach: MSMEs often have limited access to wider markets, especially for export-oriented businesses. This can limit their growth potential.
- Competition: MSMEs face competition from larger enterprises, including multinational corporations, which can be challenging to compete against in terms of resources and scale.
- Regulatory and Compliance Burden:
- Complex Regulations: Navigating a web of complex regulations can be challenging for MSMEs, diverting their attention and resources away from core business activities.
- Compliance Costs: Compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements can be expensive, especially for small businesses with limited financial resources.
- Lack of Skilled Labor:
- Skill Shortages: Finding and retaining skilled employees can be difficult for MSMEs, particularly in specialized industries.
- Training Costs: Training and upskilling employees can be costly for small businesses.
- Access to Technology and Innovation:
- Limited Research and Development: MSMEs may struggle to invest in research and development, limiting their ability to innovate and stay competitive.
- Technology Adoption: Keeping up with technological advancements can be challenging for resource-constrained MSMEs.
- Financial Management and Literacy:
- Inadequate Financial Management: Many MSME owners lack the financial knowledge required to manage their businesses effectively, leading to poor financial decisions.
- Lack of Access to Credit Information: Limited access to credit histories and credit scoring mechanisms can make it difficult for MSMEs to secure loans.
- Market Fluctuations and Economic Uncertainty:
- Vulnerability to Economic Cycles: MSMEs, particularly those in sectors sensitive to economic changes, can be disproportionately affected during economic downturns.
- Access to Government Support:
- Awareness and Access: Some MSMEs may not be aware of or have access to government schemes and support programs designed to assist them.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:
- Dependency on Key Suppliers: Reliance on a few key suppliers can leave MSMEs vulnerable to supply chain disruptions.
Technology is the game changer in unlocking the potential of MSMEs
Nano businesses, which primarily operate in the informal sector, encounter unique challenges that call for customized solutions. These businesses are incredibly small, often generating daily sales as low as Rs. 2,000. They frequently lack the necessary documentation to qualify for formal credit, and their inability to provide collateral further complicates their access to loans. Their credit requirements typically fall within the range of Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 5 lakh, rendering them less appealing to larger financial institutions due to the impractical cost of processing such small loans.
However, there is a silver lining to this scenario. A huge number of small business owners are equipped with smartphones, opening up a vast opportunity for microfinance companies and fintech firms to introduce paperless banking and financing solutions directly to their customers. By adopting innovative and collaborative approaches, these modern-age lenders are bridging the gap for small businesses that lack conventional financial records, granting them access to credit and fostering growth. To overcome the challenge posed by the absence of income documentation, lenders are exploring alternative methods of credit assessment, placing a primary emphasis on evaluating the borrower’s “willingness to pay.” Over time, they gradually incorporate the assessment of “ability to pay” with higher credit amounts in subsequent lending transactions.
Lenders are harnessing data from various sources to construct comprehensive scorecards for credit underwriting. This is an ongoing process, constantly refining as more variables and trends emerge during the customer onboarding, lending, and repayment phases. The partnership between lending institutions and fintech companies has successfully addressed the cost issue by facilitating effective credit risk assessment. Credit decisions now rely on automated algorithms, allowing for instantaneous approval and rapid disbursement, often within a matter of hours.
In addition to the above, there are other factors that are helping to widen access to credit for MSMEs. These include:
- Government Initiatives: The government has introduced various schemes to facilitate MSME lending in India. The Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) is one such initiative in which the MSME collateral-free loan limit is up to 500 lakh INR, per eligible borrower. The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) aims to support micro-enterprises by offering loans at different stages of their growth.
- Financial Literacy Programs: Various organizations and government bodies conduct financial literacy and skill development programs to empower MSME owners with the knowledge needed to manage their finances effectively.
- Sector-Specific Lending: Tailored lending programs for specific industries or sectors within the MSME category are an attempt to address the unique needs and challenges faced by these businesses.
- Collaboration with Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs): Many MSMEs are turning to NBFCs for loans due to their more flexible lending criteria. Collaborations between traditional banks and NBFCs are a boost to enhancing access to credit for MSMEs.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending: P2P lending platforms provide an alternative source of funding for MSMEs, connecting them with individual investors willing to lend money at competitive rates.
Conclusion
Unlocking the potential of MSME lending in India is essential for driving economic growth, employment generation, and overall development. By addressing the challenges faced by these enterprises and leveraging innovative financial solutions, India can empower its MSMEs to thrive and contribute even more significantly to its economy. A greater proliferation of inventive lending platforms has the potential to unleash a significantly increased influx of credit for micro and nano entrepreneurs. By harnessing technology, receiving support from the government, and operating within a sturdy regulatory framework, smaller lending institutions such as Microfinance firms can fully maximize their capabilities. This, in turn, can promote greater participation of MSMEs in contributing to overall GDP growth.
It is imperative for government bodies, financial institutions, fintech companies, and other stakeholders to work collaboratively to create an enabling environment for MSMEs to access the credit they need to prosper.
If you are looking to transform your debt collections strategy with the power of digital and data-powered insights, reach out to us to request an exploratory session at sales@credgenics.com or visit us at www.credgenics.com
FAQs:
- Who is eligible for an MSME loan in India?
Eligibility criteria for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) loans in India can vary depending on the specific lender and the type of loan or scheme. However, here are some common eligibility factors that are often considered:
- Business Classification: To be eligible for an MSME loan, your business must fall under the MSME category as defined by the government of India. The classification is typically based on factors such as the type of industry (manufacturing or service) and investment in plant,machinery, or equipment. The specific criteria for micro, small, and medium enterprises can vary, so it’s essential to check the current definitions.
- Business Registration: Your business should be registered as an MSME under the relevant government authorities or have the necessary business registration documents.
- Creditworthiness: Lenders will assess your creditworthiness, which includes factors such as your credit history, repayment capacity, and financial stability. A good credit history can increase your chances of loan approval.
- Purpose of the Loan: You should have a clear and legitimate purpose for taking the loan, such as working capital needs, business expansion, purchasing machinery, or upgrading technology.
- Business Vintage: Lenders may consider the number of years your business has been in operation. Typically, a business should have a minimum operational history to qualify for certain loans.
- Financial Documents: Be prepared to provide financial documents, including audited or unaudited financial statements, income tax returns, bank statements, and other documents that demonstrate your business’s financial health.
- Repayment Capacity: Lenders will assess your ability to repay the loan. This includes evaluating your business’s cash flow, profitability, and debt service coverage ratio.
- Collateral or Security: Depending on the loan amount and type, some lenders may require collateral or security. However, many government-backed MSME loan schemes offer collateral-free loans up to a certain limit.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Ensure that your business complies with all relevant regulatory and legal requirements, including tax filings, licenses, and permits.
- Loan Specific Criteria: Different types of MSME loans and schemes may have additional eligibility criteria specific to their objectives. For example, loans for export-oriented businesses may have different criteria than loans for technology upgrades.
- What are the opportunities for the MSME sector in India?
Opportunities for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in India are abundant and diverse, reflecting the country’s dynamic and rapidly evolving economic landscape. Firstly, India’s burgeoning consumer market presents a significant opportunity for MSMEs. With a population of over 1.3 billion people and a growing middle class, there is substantial demand for a wide range of products and services, from consumer goods to specialized niche offerings. MSMEs can tap into this vast domestic market, catering to the diverse needs and preferences of Indian consumers.
Secondly, the “Make in India” initiative, launched by the government, encourages domestic manufacturing and aims to transform India into a global manufacturing hub. This initiative offers MSMEs the chance to participate in various sectors such as electronics, automotive, textiles, and pharmaceuticals, benefiting from favorable policies, incentives, and access to global supply chains. Additionally, the push for digitization and Industry 4.0 technologies creates opportunities for MSMEs to adopt advanced manufacturing practices and boost productivity.
Thirdly, India’s emphasis on entrepreneurship and innovation provides MSMEs with a favorable environment for creativity and growth. Various government schemes and startup initiatives support new and innovative ventures, fostering a culture of entrepreneurship. Access to venture capital, angel investors, and incubation centers has made it easier for MSMEs to secure funding and mentorship. Moreover, the global outsourcing trend offers opportunities for MSMEs in information technology, business process outsourcing, and knowledge-based services, enabling them to provide cost-effective solutions to international clients.
In summary, MSMEs in India have opportunities to thrive in the vast domestic market, benefit from government initiatives to boost manufacturing and innovation, and leverage the country’s position in the global outsourcing landscape. To capitalize on these opportunities, MSMEs must focus on innovation, adaptability, and competitiveness while staying attuned to evolving market trends and regulatory changes.





