India’s booming fintech ecosystem is aligning with the ongoing regulation changes in fintech that aim to provide broader operative frameworks, protect customers, and facilitate long-term business stability. While regulatory authorities want to nurture innovation, a lack of comprehensive regulations in the past has raised concerns about consumer protection and interpretability of applicable guidelines.
The Challenge: Juggling Growth and Compliance
Currently, several regulations cover fintech business, but not many have been specifically designed for the sector, which came into prominence over the past few years. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is stepping in with a novel solution: a self-regulatory organization (SRO). In a move to address the burgeoning fintech industry, the RBI launched a framework in January to establish a self-regulatory organization (SRO).
This industry-led body will focus on two key areas:
1. Stronger Governance: The SRO will set stricter standards for fintech companies, ensuring responsible practices across the sector.
2. Bridging the Gap: It will act as an intermediary, facilitating communication between fintech members and regulators such as the RBI. This fosters collaboration and helps address the challenges for the fintech industry.
The Focus: Empowering Customers with Comprehensive Protections
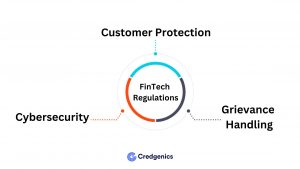
The framework primarily targets financial companies currently outside the scope of traditional regulations. This means a renewed focus on:
- Customer Protection: Ensuring fair treatment and safeguarding user data are top priorities.
- Cybersecurity: Robust measures to protect sensitive financial information will be implemented.
- Grievance Handling: Establishing clear processes for addressing customer concerns is crucial.
Benefits: For Consumers and Fintechs
The SRO framework offers significant advantages for both consumers and fintech companies:
- Clearer Rules: Fintechs will have a defined set of guidelines to follow, ensuring responsible operations.
- Enhanced Consumer Protection: Stronger customer safeguards will be implemented, addressing issues like data privacy and fair lending practices.
- Innovation Fostered: The framework aims to be flexible enough to avoid stifling innovation in this dynamic sector.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
By establishing a defined set of guidelines and standards, the framework will provide fintechs with a clear roadmap for responsible operations, while simultaneously enhancing consumer protections through the implementation of stringent safeguards.
The success of this approach hinges on several key factors:
- SRO Effectiveness: The SRO’s ability to attract members, create strong standards, and represent the market effectively will be crucial.
- Incentives and Oversight: Encouraging participation and ensuring responsible SRO operation under RBI supervision are vital.
Stricter regulations become necessary as the market and landscape matures over time. Recent regulatory action in cases like that of Paytm highlight the need for robust KYC (Know Your Customer) verification and responsible lending practices.
A Look Forward: Transparency and Stability
In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a crucial role in regulating fintech activities, including payment systems, digital lending, and cybersecurity. The RBI’s regulatory framework aims to foster innovation while safeguarding the stability and integrity of the financial system. Fintech companies operating in India must adhere to RBI guidelines, obtain the necessary licenses, and comply with regulatory reporting requirements.
The SRO framework represents a proactive approach. It aims to bring transparency to digital lending, enhance data security, and establish clear credit limits. This will ultimately improve the conduct of the sector and benefit consumers in the long run.
While some uncertainty remains, India’s self-regulatory model presents a promising path forward for fintech. It seeks to strike a balance, encouraging innovation while ensuring a secure and responsible financial ecosystem for all.
If you are looking to transform your debt collections strategy with the power of digital and data-powered insights, reach out to us to request an exploratory session at sales@credgenics.com or visit us at www.credgenics.com.
FAQs:
1. What is a self-regulatory organization (SRO) in the context of fintech?
An SRO is an industry-led organization that sets best practices and oversees the conduct of its members in the fintech sector. It acts as a bridge between fintech companies and regulators like the RBI.
2. What are the benefits of the SRO for fintech companies?
- Clearer Rules: The SRO will establish a defined set of guidelines for responsible operations, reducing regulatory uncertainty.
- Enhanced Image: Adhering to SRO standards can increase legitimacy and gain “regulatory comfort” from the RBI.
- Improved Communication: The SRO can facilitate smoother communication between fintechs and regulators.
3. How does the SRO framework benefit consumers?
- Stronger Protections: The framework focuses on customer protection, including data privacy and fair lending practices.
- Increased Transparency: Clearer rules and oversight enhance transparency within the fintech sector.
- Improved Grievance Handling: The SRO can help establish clear procedures for addressing consumer concerns.
4. What are some potential challenges of the SRO model?
- Effectiveness of the SRO: The SRO’s success hinges on its ability to attract members, create strong standards, and effectively represent the market.
- Incentivizing Participation: Encouraging fintech companies to join and adhere to SRO guidelines is crucial.
- Long-Term Sustainability: As the market matures, stricter regulations might be needed alongside the SRO framework.
5. What does this mean for the future of India’s fintech industry?
The SRO model represents a proactive approach towards regulating the rapidly growing fintech sector. It aims to foster innovation while ensuring a secure and responsible environment for both consumers and businesses. The success of this model will depend on effective implementation and adaptation to the evolving market landscape.





