A multifinance company (MFC) is a type of financial entity that provides a range of financial services and products to businesses and individuals. They offer consumer loans, working capital loans, lease financing, and factoring. In some cases, they may also offer investment services and insurance. MFIs exist as standalone companies, although prominent banks have their own multifinance programs and services. Banks, foreign exchange services, insurance, and multifinance companies operate simultaneously in the economic landscape, benefiting small-scale businesses and the underbanked population segments.
Even though both banks and MFIs perform the function of issuing and leasing funds to their respective borrower base, they operate differently. While banks can retrieve cash directly from customers, MFIs can only recover loan money from their customers and are not licensed to accept deposits from the public. They raise funds from loans, bonds, and other debt instruments. Another differentiating factor between banks and MFIs is that the latter have more flexibility in their lending criteria, and may also lend to customers with lower credit scores or those who do not meet collateral requirements.
A common means of obtaining credit in Indonesia, multifinance companies are contributing significantly to the success of micro, small, and medium-sized businesses (MSMEs), which depend on fund leasing activities to carry out their daily operations. These enterprises must purchase or rent essential properties, such as heavy utilities, to conduct business activity. They interact with multifinance companies in this particular niche to facilitate the same. As a result, the total loan value of MFIs in Indonesia has seen a steady increase.
Source: CEIC Data
Regulatory landscape of MFIs in Indonesia
Similar to banks, MFIs are regulated by Otoritas Jasa Keuangan (OJK, or Financial Services Authority) of Indonesia. Prior to the establishment of OJK in 2011, MFIs were under the supervision of Bapepam. OJK issued 28/POJK.05/2014 to regulate the licensing and supervision of multifinance companies in Indonesia. This is due to the importance of multifinance in the larger economic scheme. Since many businesses rely on MFIs to buy and hire equipment for their operations, the Indonesian government is directly involved in their supervision. Multifinance companies are, therefore, obligated to operate within the regulatory framework laid out by the government to ensure the businesses’ longevity and compliance.
As per the regulation cited above, entities have to follow a number of steps to be incorporated as a multifinance company and are required to fulfil several criteria pertaining to minimum capital, membership, labor restrictions, and ownership.
Present market scenario in Indonesia
According to data published by OJK, the net financing by multifinance companies grew by 14.57% YoY as of January 2023. This indicates the immense potential for further expansion and collaboration with several industry segments in Indonesia.
Currently, the MFI ecosystem is contributing the most to the automobile industry in Indonesia. The prices of many automobiles have risen in recent years, compelling MSMEs to find new alternatives to cover the rise in costs. Through multifinance companies, customers only need to pay the down payment to the dealer, instead of the previously agreed interest rate on the automobile they may have bought before.
Other than the automobile sector, multifinance companies’ role has expanded over the years. A rising number of MSMEs are using heavy utilities with each passing year, and many of these ventures have partnered with MFIs across sectors. One of them is investment financing, whose role has become popular in providing finance for new business ventures. MFIs that finance the investment in such ventures also provide funding for the infrastructural financing, which is vital for growth.
In the long run, the working capital financing segment will also stand to benefit from the presence of MFIs. MFIs can provide a substantial amount of working capital to these ventures based on previously agreed terms and conditions under OJK’s supervision. They may also provide credit support for the financing of various projects initiated by the government, such as Kredit Usaha Rakyat (People’s Business Credit).
Multifinance companies and financial inclusion in Indonesia
The financial services industry in Indonesia has made good progress in reaching out to the underserved population. However, there is a pressing need to reach out further to the unbankable population. As per a 2022 report, Indonesia ranked 28th on the Global Financial Inclusion Index, validating that Indonesia lags behind several other developing countries in terms of financial inclusion. This indicates a vast scope for tapping into unbanked markets in the country, to enable more segments to avail themselves of the benefits of multifinance.
Education and poor infrastructure are reasons these markets remain isolated from the rest of the world. Moreover, complex geography makes it difficult for many financial institutions to set up new branches in many areas of the country. Since the operating costs of setting up new businesses in these areas outweigh the benefits, development is slow and inconsistent. Since multifinance companies have a reach in both rural and urban areas, they can help cover the gap. The government’s push toward improving financial inclusion paves the way for multifinance companies to meet the financing needs of lower-income households.
Expansion of the MFI ecosystem through technology
The Digital Finance Innovation Roadmap and Action Plan 2020-24 launched by the OJK is expected to provide a boost to multifinance players to utilize the wide range of emerging technological capabilities, tap into a whole new segment of customers, and in turn increase financial inclusion. With advancements in technology, digital lending and e-commerce activity are expected to show upward trends. 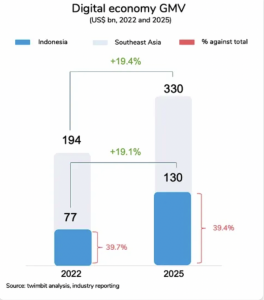
Source: Twimbit analysis
The changing market landscape is propelling a transition and adoption of new systems powered by digitization. Multifinance firms in Indonesia have the opportunity to innovate and digitize their processes. Creating an online presence in the financing market will offer MFIs the chance to expand borrower base and lending portfolios. The roadmap made by OJK aims to further support innovation in the digital space, and will create more opportunities for multifinance collaboration.
FAQs:
- What is a multi finance company?
A multi finance company is a lending institution in Indonesia that provides credit to businesses and individual borrowers to conduct a service or purchase a product. They differ from banks in that they do not perform a deposit-accepting role and can only recover loan repayments from the debtors.
- Do banks and Multifinance companies perform the same role in Indonesia?
MFIs are different from banks because, even though both lend money to the public, MFIs are not licensed to accept cash deposits. MFIs raise funds by issuing debt securities and through capital invested by company owners and investors. Additionally, MFIs are more flexible and risk-taking in their lending criteria and offer loans even to customers who fall short of collateral requirements or do not have a robust credit history.
- Who regulates the Multifinance companies in Indonesia?
OJK (Financial Services Authority) is the regulatory body for all multi finance companies in Indonesia. All stages of establishing an MFI, including incorporation, ownership, membership, and other compliance requirements, are supervised by OJK.





