Corporate executives, academics, policymakers, and a host of other professionals are trying to identify new opportunities to leverage AI technology, a transformative force with implications for learning, the workplace, and beyond. Within the corporate realm, AI stands as a catalyst for redefining customer interactions and supporting business growth. Businesses are exploring how this technology might reshape various facets of their operations, spanning sales, customer service, marketing, commerce, IT, legal, HR, and more.
Nevertheless, senior IT leaders face the imperative challenge of establishing a secure and trustworthy means for their workforce to embrace these technological advancements. As per a research by Harvard Business Review, an overwhelming 79% of senior IT leaders have voiced their apprehensions regarding the potential security risks introduced by these technologies, while 73% harbor concerns about the potential for biased outcomes. On a broader scale, organizations must underscore the necessity of upholding ethical, transparent, and responsible deployment of these transformative technologies, effectively managing the risk of AI.
The need for managing the risk of AI
Using AI technology within an enterprise setting diverges significantly from individual consumer use. Businesses must operate within the confines of industry-specific regulations, particularly in some sectors. Navigating this terrain is difficult and fraught with legal, financial, and ethical ramifications, particularly if the content produced turns out to be unreliable, inaccessible, or offensive.
For instance, the potential consequences of an AI chatbot offering incorrect instructions are vastly different from when it provides guidance to a field service worker on repairing heavy machinery. The disparity in risk emphasizes the need for clear ethical standards in the development and application of generative AI because it has the potential to have negative consequences and, in extreme cases, actually cause harm.
To effectively harness AI, organizations must establish a comprehensive and actionable framework. This framework should harmonize AI objectives with the core functions their business aims to accomplish. This alignment encompasses the impact of AI on various business facets, such as sales, marketing, commerce, service, and IT roles.
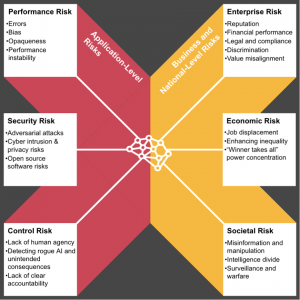
Source: PwC
Strategies for managing the risk of AI
Managing AI risks in the Indian business context requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. Here are some strategies that businesses managing the risk of AI are adopting:
1. Comprehensive risk assessments
Leaders tasked with managing AI adoption within their organization should proactively identify potential risks associated with this adoption. They ought to establish a comprehensive risk assessment framework, encompassing critical areas such as data security, ethical considerations, and adherence to regulatory requirements. It is crucial to ensure that this risk assessment framework remains a dynamic and responsive tool. To achieve this, they should commit to regular updates and revisions to stay aligned with the evolving landscape of AI technologies.
2. Data governance and protection
The implementation of robust data governance frameworks is of paramount importance in today’s data-driven landscape as organizations grapple with the twin imperatives of data privacy and security. These frameworks serve as the foundational infrastructure for overseeing the entire lifecycle of data within an organization, including its collection, storage, processing, and sharing. While ensuring data privacy and security, organizations must adhere to a multifaceted approach that combines various elements, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits.
Encryption, for instance, plays a pivotal role in safeguarding data against unauthorized access and breaches. Using this method, data is converted into a form that can only be decrypted by authorized users who possess the necessary keys or credentials. It acts as a digital shield, rendering data indecipherable to anyone without the proper access rights. Consequently, even if a malicious actor intercepts the data, they will be confronted with an unintelligible string of characters.
Access controls represent another critical facet of data governance. Organizations must implement stringent access controls to manage who can access specific datasets and what actions they can perform with that data. This involves the creation of user profiles and permissions, which limit access exclusively to authorized personnel. By exercising tight control over data access, organizations can significantly mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized data breaches. Routine monitoring of user activities also contributes to early detection of unusual or suspicious behaviors, enabling proactive security responses.
Regular audits, a core component of data governance, are instrumental in evaluating the effectiveness of an organization’s data protection measures. Through systematic and recurring audits, an organization can identify vulnerabilities, potential risks, and compliance issues. Auditors examine security protocols, access logs, and data handling procedures to ensure that they align with best practices and compliance requirements. By conducting regular reviews and assessments, organizations can identify and rectify any security or compliance gaps, preventing them from escalating into security breaches or violations of data protection regulations.
It is imperative that organizations remain informed about data protection regulations and steadfastly adhere to them. Data protection laws are not static; they continuously evolve to address emerging threats and privacy concerns. Failure to adhere to these regulations can have legal consequences, including hefty fines and penalties. Staying informed about these evolving laws and ensuring compliance is a vital element of data governance.
3. Developing an AI ethics framework
Establishing a comprehensive code of ethics for AI usage within the organization is a foundational step towards responsible and ethical AI adoption. This framework should be thoughtfully designed to address ethical considerations, encompassing fairness, accountability, and transparency. Fairness, in the context of AI, pertains to ensuring that AI systems do not discriminate against certain individuals or groups and that they provide equitable opportunities and outcomes. Accountability involves defining roles and responsibilities for AI-related decisions and actions, making it clear as to who is answerable for any potential consequences.
Transparency is another pivotal aspect, signifying that the organization should prioritize clarity and openness in AI decision-making processes. This means that the inner workings of AI algorithms should not be shrouded in obscurity, and stakeholders, including employees, should be able to understand how AI systems arrive at their conclusions. Moreover, the code of ethics should extend to encompass the ethical implications of AI in areas such as data privacy, security, and the potential displacement of human jobs.
In tandem with establishing this ethical framework, it is imperative to ensure that employees are well-versed in these principles. This can be achieved through training, workshops, and ongoing education. Employees need to comprehend the ethical considerations associated with AI adoption, and they should be equipped to make informed and responsible decisions when working with AI systems. By fostering an organizational culture that prioritizes ethical AI use, business leaders not only mitigate risks but also build trust among employees, customers, and stakeholders, reinforcing commitment to ethical AI practices.
4. Collaborating with regulators
Engaging with regulatory bodies is a strategic move for organizations looking to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of AI regulations. It entails proactive communication with authorities in charge of formulating AI-related policies, allowing the organization to learn about the most recent changes and requirements in the law. With this engagement, leaders position their organization to stay ahead of the curve in terms of compliance, thus reducing the risks associated with non-compliance and potential legal ramifications.
This collaborative approach extends beyond mere adherence to existing regulations. It provides an opportunity for the organization to actively contribute to the development of responsible AI guidelines. By sharing insights, best practices, and ethical considerations, they can influence the creation of industry-specific standards that align with the organization’s values and objectives. This proactive involvement not only helps shape the regulatory landscape but also allows the organization to play a part in defining the ethical and responsible use of AI technologies. The development of a coordinated and favorable environment for AI innovation while ensuring compliance with statutory requirements and industry standards depends on the cooperative synergy between organizations and regulatory bodies.
5. Investing in training and skill development
Investing in training programs is a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to bridge the prevailing talent gap in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). The rapid evolution of AI technologies has given rise to a demand for specialized skills and expertise, which often outpaces the available talent pool. Recognizing this, organizations should commit to initiatives that aim to upskill their existing workforce or collaborate with reputable AI training institutions. These initiatives have the dual benefit of not only addressing the talent shortage but also ensuring that your team possesses the essential expertise required to effectively manage the risks associated with AI adoption.
Upskilling the existing workforce is an effective strategy to harness untapped potential within the organization. By providing training programs that equip employees with AI-specific knowledge and skills, leaders empower them to better understand AI technologies, their implications, and their potential risks. This enables the team to engage in more informed decision-making, contribute to the development of ethical AI frameworks, and effectively manage AI projects within the organization. Moreover, investing in the workforce’s professional development fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, ensuring that the team remains agile and well-prepared to navigate the evolving AI landscape.
6. Continuous monitoring and evaluation
Regular and diligent monitoring of AI systems is a fundamental practice that organizations must embrace to ensure the ongoing health and effectiveness of their AI implementations. Through systematic and routine evaluation, organizations can swiftly detect and address any emerging issues, vulnerabilities, or discrepancies in AI performance. This proactive approach enables timely intervention, reducing the potential for operational disruptions or adverse consequences.
Simultaneously, it is vital for organizations to establish well-defined procedures for managing the risk of AI-related incidents and vulnerabilities. These protocols should outline the steps to be taken when issues arise, encompassing incident reporting, investigation, mitigation, and resolution. A clear incident response framework is essential to minimize the impact of AI-related incidents and prevent their recurrence.
7. Building resilience
In anticipation of AI-related challenges, organizations should proactively develop contingency plans and resilience strategies. To effectively handle unanticipated AI failures or issues, these preparedness measures also include the creation of backup systems and crisis response protocols. By having these safeguards in place, organizations can minimize disruptions and swiftly address AI-related setbacks, ensuring continuity of operations and mitigating potential risks. Such proactive planning also enables organizations to increase their general resilience in the face of AI-related difficulties, ultimately improving their capacity to successfully and confidently navigate the dynamic AI landscape.
Conclusion
The pursuit of AI adoption in the corporate landscape holds tremendous promise, offering transformative potential in diverse sectors. However, this journey is not without its challenges, particularly in navigating the complexities of AI risks within the Indian business context.
Senior IT executives and organizations must approach the adoption of AI with a defined and clear strategy that includes in-depth risk assessments, effective data governance and protection measures, the development of an ethical framework, proactive engagement with regulatory bodies, and investments in training and skill development.
These strategies serve as the foundation for managing the multifaceted landscape of AI risks, including data security, ethical considerations, and compliance with evolving regulations. By adhering to these principles, organizations can harness the power of AI while minimizing potential pitfalls and ensuring a responsible, secure, and ethical AI adoption process.
In doing so, they not only protect themselves from potential harm but also set the stage for fostering trust, innovation, and ethical AI practices. The dynamic landscape of AI technology continues to evolve, and by staying proactive and vigilant, organizations in India can lead the way in responsible AI adoption, driving growth and innovation while safeguarding their employees, customers, and stakeholders.
If you are looking to transform your debt collections strategy with the power of digital and data-powered insights, reach out to us to request an exploratory session at sales@credgenics.com or visit us at www.credgenics.com
FAQs:
1. How do you mitigate the risk of artificial intelligence?
Mitigating the risks associated with artificial intelligence (AI) involves a multifaceted approach aimed at safeguarding data privacy, security, and ethical considerations. Here are several key strategies to mitigate AI risks:
- Comprehensive risk assessment: Organizations can begin by conducting a comprehensive risk assessment specific to their AI initiatives. They should identify potential risks, vulnerabilities, and threats associated with AI systems and their applications within the organization. This assessment should include data security, ethical considerations, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Data governance and protection: Implementing robust data governance frameworks to ensure data privacy and security is the next step. This includes defining data ownership, access controls, and data lifecycle management. Regular audits and compliance checks are essential to maintain data integrity and mitigate potential breaches.
- Ethical framework: Establishing a clear code of ethics for AI usage within the organization is crucial This framework should address fairness, accountability, transparency, and other ethical considerations. Businesses should ensure that employees are well-versed in these principles through training and awareness programs.
- Engaging with regulators: Organizations must collaborate with regulatory bodies to stay informed about evolving AI regulations and contribute to the development of responsible AI guidelines. Proactive engagement with authorities responsible for shaping AI-related policies helps the organization align with legal requirements and industry standards.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation: Regularly monitoring and evaluating AI systems to detect and address issues promptly. Developing clear procedures for handling AI-related incidents and vulnerabilities is necessary. Transparency and accountability are crucial in this process.
2. Why is it essential to have a code of ethics for AI use within an organization?
Having a code of ethics for AI is essential to ensuring responsible and ethical AI adoption. It helps organizations address fairness, accountability, transparency, and other ethical considerations, promoting equitable and responsible AI practices. Such a framework guides employees in making informed and ethical decisions when working with AI systems and fosters trust among stakeholders.
3. How can organizations stay compliant with evolving AI regulations?
Organizations can stay compliant with evolving AI regulations by actively engaging with regulatory bodies and seeking insights into the latest developments and requirements. This proactive communication helps organizations align with legal requirements and industry standards, reducing the risks associated with non-compliance and potential legal ramifications. It also provides an opportunity to contribute to the development of responsible AI guidelines.
4. Why is data governance crucial to mitigating AI risks?
Data governance is crucial because it ensures the privacy and security of sensitive information. By defining data ownership, access controls, and data lifecycle management, organizations can protect data from unauthorized access and breaches. Regular audits and compliance checks are essential to maintaining data integrity and mitigating potential data security risks associated with AI adoption.




