Technology is widely regarded for its role in driving innovation in operational processes and customer experiences along with an overall futuristic evolution of industries. As we reflect on the debut of ChatGPT, it is evident that this technological development has also been a remarkable turning point. With ChatGPT, the world witnessed extraordinary capabilities of a language model (LLM) generative AI, propelling this remarkable technology into the global spotlight. Advancements in deployment of Generative AI in banking sector have led to several aspects of banking being bolstered through this disruptive technology.
Generative AI represents a category of artificial intelligence designed to remodel content using existing data, be it text, images, music, or even videos. These AI models are trained on vast volumes of written, visual, and auditory data, absorbing patterns and structures within the vast information at their disposal. The most common interface for interacting with an LLM GenAI is through natural language text, where users articulate their desires or inquiries, sparking the AI’s creative output.
Over the years, the financial services industry has witnessed significant changes driven by innovations such as online banking and mobile apps. However, one of the most transformative developments in recent years has been the integration of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) into banking operations. The way banks interact with customers, manage data, identify fraud, and make decisions has been significantly impacted by generative AI, which is powered by deep learning models like GPT.
The magnified role of Generative AI in banking sector
As per a McKinsey survey, 40% of the respondents said they will increase their organization’s investment in AI because of advances in Generative AI. Companies across many industries, particularly in the financial sector, are incorporating this game-changing technology into their line of products as a result of the increased public awareness of GenAI. Each one is trying to adopt this innovation from a unique angle, tailored to their core business focus.
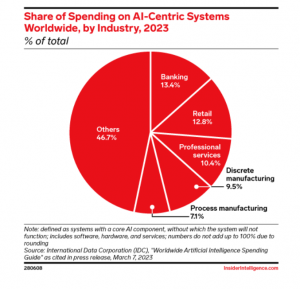
Source: Insider Intelligence
To comprehend the current role and value of GenAI, it is imperative to trace the technological advancements that the banking industry has adopted over the past decade. A decade ago, the onset of digital transformation compelled banks to reconfigure their approach to delivering business-to-consumer (B2C) services. Customers began to demand easier access to their banking services via online and mobile applications, anytime and anywhere. This shift in customer expectations reverberated across all facets of banking, spanning retail, corporate, investment, and private banking. The landscape further transformed with the advent of Open Banking, adopted by numerous nations. The widespread adoption of digital banking services at varying levels of maturity across regions subsequently paved the way for the rise of technology start-ups, collectively known as fintech companies. These entities sought to disrupt and innovate within the financial services sector, reshaping the industry as we know it.
Fintech companies have introduced a wave of innovative digital banking services, often catering to specific niche markets. Concurrently, the emergence of challenger and neo-banks has placed pressure on established, traditional banking giants. These traditional institutions, despite possessing a huge amount of client data and valuable assets, have encountered significant hurdles in adapting to the digital era due to their legacy operational models and core banking systems.
The lack of agility in traditional banking often compelled them to explore alternative avenues, including the creation of their own neo-banks, as they recognized the need to compete effectively in the rapidly evolving financial landscape. These endeavors allowed them to swiftly construct entirely new banking services, a feat that proved more efficient than attempting to overhaul their existing banking infrastructure. Despite the undeniable importance of digital banking services in modern banking, these services can only reach their full potential when combined with data-driven insights. The real competitive advantage in the banking sector lies in the fusion of cutting-edge digital banking experiences with the unparalleled wealth of historical customer data possessed by traditional banks. This synergy represents their true value proposition, differentiating them in the competitive banking arena.
Deploying generative AI in banking processes
From automating routine tasks to enhancing customer experiences and mitigating risks, the applications of Generative AI in banking are both diverse and promising. Some of the ways in which generative AI can be deployed in banking are:
- Enhanced customer experience: Throughout the past decade, banking institutions across all customer-facing channels, be they retail, corporate, wealth management, or private banking, have made significant strides in introducing digital banking services. These services, accessible through online platforms or mobile applications, have been a response to the evolving demands of the market. However, what’s noteworthy is that the majority of these digital banking experiences, in various banking segments, still relied heavily on human intervention, with customer service representatives offering advice, insights, and recommendations.
Even in cases where banks incorporated chatbots and virtual assistants as part of their digital customer engagement strategies, the interactions were often limited to basic “ask-and-respond” exchanges. It was only with the advent of conversational and generative AI that these experiences underwent a remarkable transformation and became more human-like, versatile, intelligent and engaging. Generative AI, often referred to as GenAI, has since captured the imagination of the general public, thanks to its multifaceted capabilities—a blend of various AI disciplines such as natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLM).
In the realm of customer service, the integration of GenAI has become a pivotal innovation. Banks now employ GenAI services coupled with conversational AI solutions to enhance or establish chatbot and virtual assistant interfaces. At the heart of GenAI lies the formidable LLM capability, which equips both digital assistants and human customer service advisors with insights into individual customers, their inquiries, and the most suitable banking services to address their unique needs.
2. Tailored product offerings: Crafting tailored financial solutions for individuals across retail and private banking sectors, as well as catering to the unique requirements of corporate banking clients, represents a distinctive approach that can bring a new era of competitive advantage. The wealth of data at a bank’s disposal, encompassing both individual customer profiles and collective preferences of specific demographics, enables the institution to offer personalized financial recommendations or customize retail products to cater to the precise needs of each individual on a scale that was previously unattainable through digital services.
Generative Artificial Intelligence stands at the forefront of enabling these personalized banking services, manifesting through digital interactions on online platforms, mobile applications, or as an invaluable tool supporting front-office bank personnel during customer engagements. While it can readily provide recommendations in response to client inquiries via chatbots and digital assistants, it also empowers sales teams to take the initiative by devising and proposing one or more tailored bank offerings to clients.
3. Efficiency in risk assessment: In the middle office functions of a bank, another vital area where Generative Artificial Intelligence emerges as a value-added asset is the realm of risk management. Traditionally, risk management has been a multifaceted and demanding domain, characterized by activities that often surpass the department’s capacity to keep pace. Banks have used automation technologies to reduce risk exposure, particularly in response to the introduction of increasingly complex and varied digital banking services.
However, GenAI, complemented by the capabilities of explainable AI (XAI), can provide guidance to risk and fraud detection teams. It does so at a scale that can alleviate the overwhelm experienced by many such teams. Vital functions like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies, central to a bank’s risk management and customer verification efforts, stand to benefit immensely from GenAI’s capabilities.
4. Automation of compliance: As the regulatory landscape continually evolves and banks introduce new financial products, the operational landscape often encounters friction points. Compliance regulations, in particular, can introduce complexities that necessitate meticulous attention. With the democratization of digital banking channels, granting various types of bank customers access to a wide array of sophisticated financial products, the volume and pace of compliance activities have surged significantly.
Generative Artificial Intelligence in the banking sector emerges as a critical resource for bolstering the capabilities of compliance teams. It empowers these teams to navigate the expanding landscape with increased scale, sophistication, and efficiency. GenAI can undertake a spectrum of compliance-related tasks, including generating risk assessments, reviewing and refining compliance policies and procedures, producing compliance reports, and addressing regulatory inquiries.
5. Support to accounting teams: Within the bank’s back office, the accounts department assumes a role that can be argued as the lynchpin of the institution’s entire operation. Its responsibilities encompass a multifaceted array of tasks that collectively shape the bank’s financial integrity and compliance with the extensive web of banking regulations.
At its core, this department is tasked with the meticulous upkeep of precise financial records and the generation of financial reports, all executed in strict accordance with banking regulations governing the industry. To achieve this, the department diligently oversees the bank’s general ledger, ensuring its balance through reconciliation and the posting of transactions to their respective accounts. Additionally, the accounts department shoulders the responsibility of managing all tax-related activities. This includes tax planning, the calculation of tax liabilities, the filing of tax returns, and the adjustment of the bank’s operational strategies in response to ever-evolving tax laws and regulations. This strategic acumen not only minimizes risk and guarantees compliance but also optimizes the bank’s tax strategies to enhance overall financial performance.
GenAI can serve as a proactive advisor in taxation. By reviewing prevailing tax laws and regulations with historical data, it can offer insights into optimizing tax strategies and generate compliance reports with remarkable efficiency. During audit procedures, GenAI conducts audit trail analyses that adapt to evolving scenarios and inquiries posed during the audit process. In essence, the incorporation of Generative AI within the accounts department of banks promises to elevate operational efficiency, enhance compliance adherence, and augment the institution’s overall financial acumen.
6. Efficient underwriting: The bank’s underwriting department has to deal with a high influx of loan and credit applications, escalating volumes, and swifter processing demands. This dynamic has led to a need for shorter risk assessment and evaluation cycles to keep pace with the burgeoning demand.
The underwriting department plays a pivotal role in the authorization of credit products for clients, including tasks such as conducting a rigorous risk assessment of the applicant, scrutinizing associated documentation with due diligence, collaborating with front-office teams to structure loans, and implementing measures to mitigate application-related risks. In addition, the department maintains meticulous records in adherence to the bank’s underwriting guidelines.
The nature of these tasks is inherently intricate, demanding sophisticated data assessments and modeling capabilities to ascertain the authenticity and suitability of the applicant within the framework of the bank’s risk profile. By automating the exhaustive data analysis of both structured and unstructured data, GenAI empowers underwriters to devote their attention to the more intricate and unique scenarios that often require human expertise.
GenAI has the capacity to generate comprehensive risk assessments and scores by drawing insights from financial statements, credit reports, and market trends. It provides underwriters with a comprehensive information repository, enabling them to make informed assessments and decisions. GenAI can easily adapt to the dynamic nature of underwriting, readily addressing any additional questions or concerns that may arise from the content it generates.
Conclusion
Generative AI is currently in its infancy, and its true potential is yet to be fully realized as enterprises increasingly incorporate it into their operations. While the technology offers tremendous prospects of elevating banks’ efficiency, effectiveness, and customer-centricity, it also demands a meticulous approach to address challenges such as security and the emergence of AI-generated misinterpretations. As the banking landscape evolves, it will become evident that Generative AI and banking are destined to become an example followed by all financial institutions. The critical question that looms is not whether, but how early adopters will harness this capability to elevate their market standing and expand their reach among customers. The future undoubtedly belongs to those industry leaders who deftly leverage Generative AI’s transformative potential to navigate the evolving current trends of the banking industry, redefining what’s possible and reimagining the very essence of banking itself.
If you are looking to transform your debt collections strategy with the power of digital and data-powered insights, reach out to us to request an exploratory session at sales@credgenics.com or visit us at www.credgenics.com
FAQs:
- How is generative AI adding value to banks?
Generative AI is adding substantial value to banks in several key ways:
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: Generative AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants offer personalized and real-time interactions with customers, improving customer service and engagement.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation of routine tasks, data analysis, and report generation frees up human resources and reduces operational costs.
- Risk Mitigation: Generative AI assists in risk assessment and fraud detection by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying anomalies, and offering predictive modeling for risk scenarios.
- Compliance and Reporting: It helps banks stay compliant with ever-evolving regulations by generating compliance reports and ensuring adherence to guidelines.
- Product Customization: GenAI enables the creation of tailored financial products and services based on customer data and preferences, boosting cross-selling and revenue.
- Audit and Analytics: It supports audit processes, conducts financial statement analysis, and offers deep insights into data, improving financial performance.
- Efficient Underwriting: GenAI automates data analysis, allowing underwriters to focus on complex cases, resulting in faster processing and more accurate decisions.
- Market Analysis: It helps banks monitor market trends, simulate scenarios, and make informed decisions based on real-time data and predictive modeling.
2. What are the major applications of AI in banking sector?
AI is revolutionizing the banking sector by enhancing efficiency, security, and customer experiences. Here are five key applications of AI in banking sector:
- Customer Service Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots provide real-time customer support, answer inquiries, and assist with routine banking transactions. They’re available 24/7, improving customer service accessibility.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms analyze transaction data in real-time to detect unusual patterns or potential fraud. This helps banks prevent unauthorized transactions and protect customer accounts.
- Credit Scoring: AI assesses customer creditworthiness by analyzing a wide range of data, including credit history, income, and behavior. This leads to more accurate and fair credit decisions.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI algorithms analyze customer data to offer personalized product and service recommendations, such as investment options or loan offers, increasing cross-selling opportunities.
- Risk Management: The use of AI in banking sector helps manage and mitigate risks by analyzing market trends, credit risks, and economic indicators. It provides predictive insights, allowing banks to make informed decisions and optimize their portfolios.
These applications not only improve operational efficiency but also enhance the overall customer experience, making the future of AI in banking sector encouraging and promising.





